场地的复兴,长城沿线社区的重生
中国长城是世界上最重要的文化遗产资源之一,但这一古老的宝藏面临着生态环境恶化、旅游机会减少、周边社区经济衰落等问题。基于对历史和文化遗产的分析,广泛的公众参与,规划策划了一条长达258公里的大同古长城文化遗产廊道实施方案,为振兴工作绘制了蓝图。植根于该地区的景观和非凡的文化遗产,规划团队开始了重大的生态修复工程,建立了以旅游发展为目标的景区,遗产廊道的建设不仅意味着场地的复兴,更是长城沿线社区的重生。
——2019年专业奖评委会China’s Great Wall is one of the world’s most important cultural resources, but this ancient treasure faces the deterioration of the local environment, a decline in tourism opportunities, and impoverished adjacent communities. Based on historical and cultural analysis, widespread public participation, and field plan for a 258 kilometer-long Datong Ancient Great Wall Heritage Corridor creates a blueprint for revitalization. Rooted in the region’s landscape and remarkable cultural heritage, the planning team has begun the process of significant ecological remediation, the establishment of scenic areas to anchor tourism development, and the rebirth not just of place, but of community.
——2019 ASLA Awards jury
来自 BLLA 对gooood的分享。
Appreciation towards BLLA for providing the following description:
Project statement
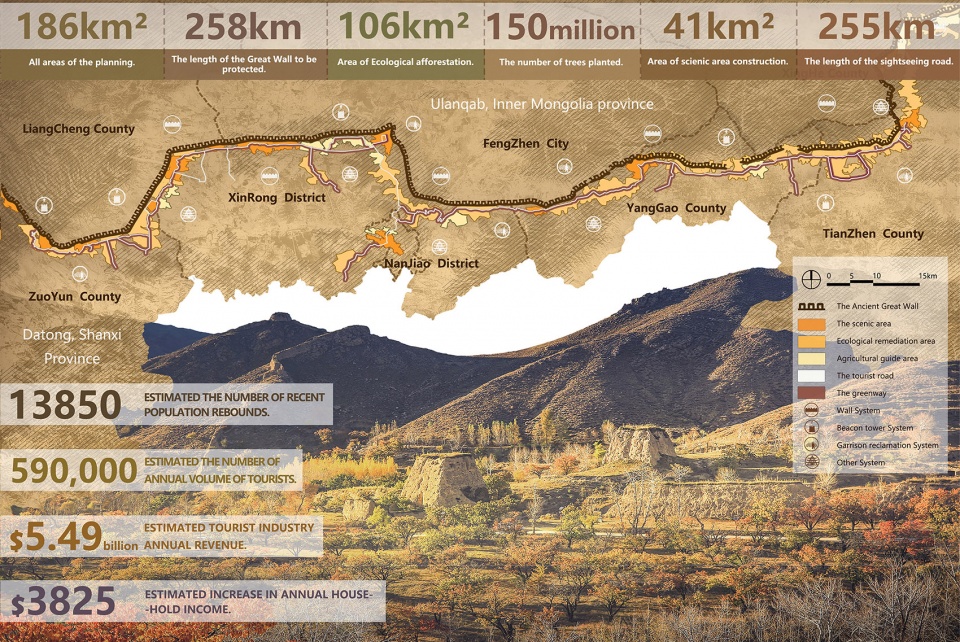
长城是世界文化遗产,人类文明宝藏。本规划沿大同古长城建立了一条长度258公里,涉及面域186平方公里的文化遗产廊道,涉及遗产保护、生态修复、文化旅游、村域经济等多项目标。
The Great Wall is a world cultural heritage, and a treasure of human civilization. The Datong Ancient Great Wall was mainly built in the Ming Dynasty (AD 1368-1644), and despite of all vicissitudes over history, its main parts have managed to remain till today. However, for all kinds of reasons, this cultural heritage has been constantly subjected to erosions and damages, and its surroundings now face deterioration of ecological environment, stagnation of tourism and poverty of residents. The planning has constructed a linear heritage corridor of 258km in length and 186km2 in area, which can realize relics protection, ecological remediation, cultural tourism, village revitalization and many other goals and would directly benefit people in the amount of 530 thousands along the route. The planning has fully invigorated the derived benefits of cultural heritages, brought a balance to the benefits in a variety of aspects of protection and development, culture and tourism, industry and ecology etc., It’s foreseeable that this particular area will be revitalized as a result of the protection and flexible development of the Great Wall.
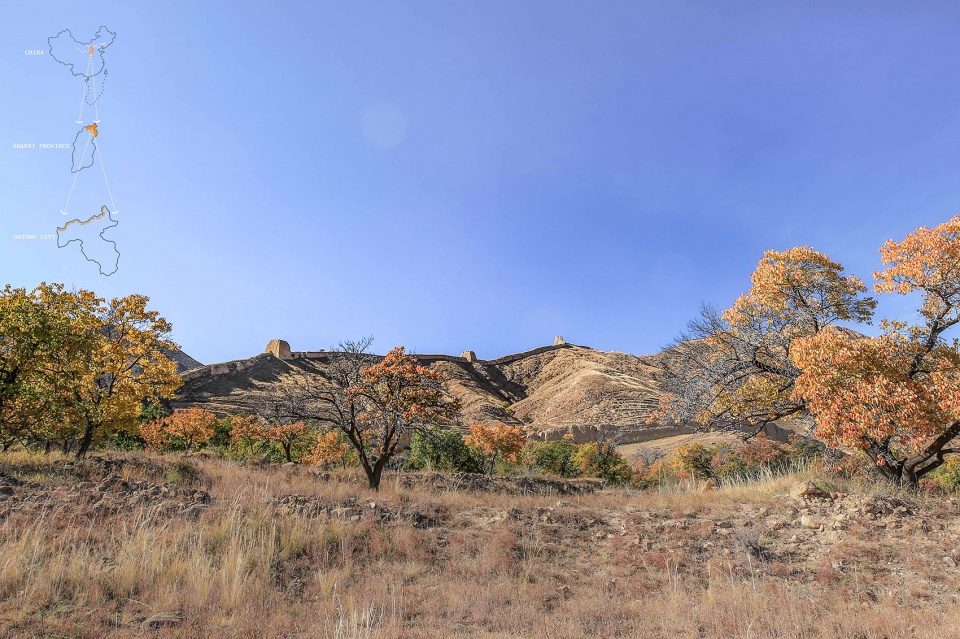
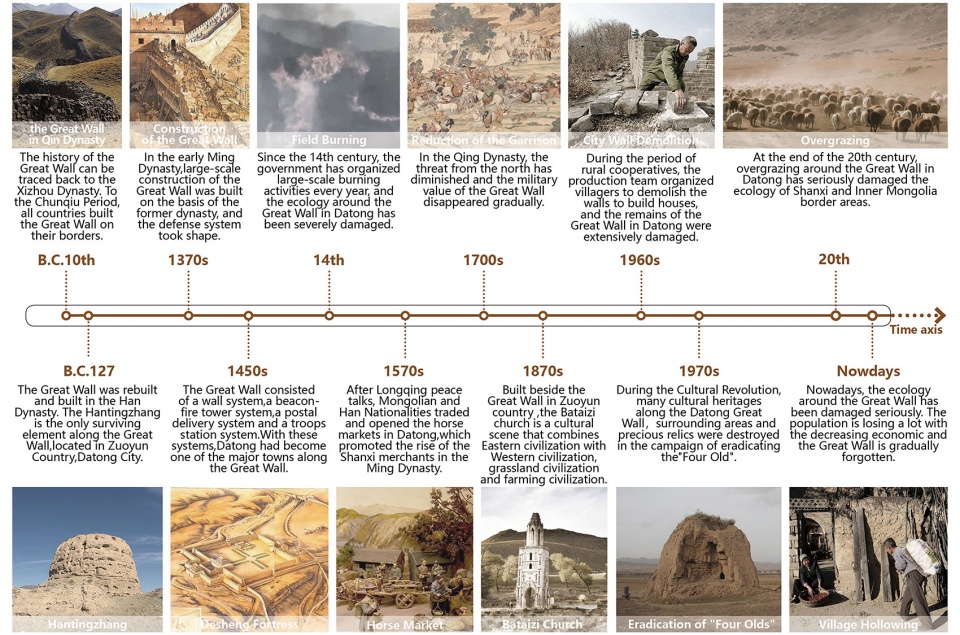
▲大同古长城的复兴:大同古长城主要为明代(AD1368-1644)建造,虽历经沧桑,依然大部分存留至今。2017年,大同市政府提出沿长城建立一条文化遗产廊道。Revitalizing the Great Wall: The Datong Ancient Great Wall was mainly built in the Ming Dynasty (AD 1368-1644), and despite of all vicissitudes over history, its main parts have managed to remain till today. In 2017, the Datong Municipal Government proposed the conception of building the cultural heritage corridor of the ancient Great Wall.
▲大同古长城历史概览:大同自古就在游牧民族和农耕民族的分界线上,长城就是农耕民族构建的一套防御体系。随着游牧民族威胁的消失,长城也日渐衰败。Historical milestones of Datong Ancient Great Wall: Since ancient times, Datong sit at the boundary of nomadic peoples and agricultural peoples, and the Great Wall served as a defense system built up by agricultural peoples. With the fading of the threats posed by nomadic peoples, the Great Wall has gradually declined day by day as well.
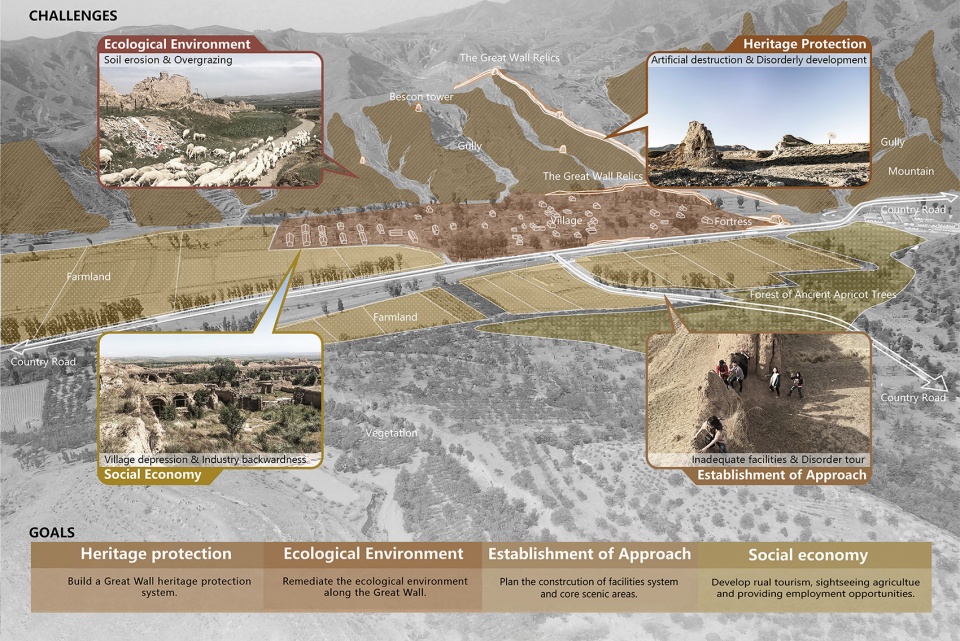
▲挑战与目标:因为种种原因,大同古长城遗产屡遭蚕食破坏,周边生态环境恶化、旅游基础设施发展迟滞、百姓生活贫困。Challenges and goals: The Datong Ancient Great Wall heritage has been constantly subjected to erosions and damages, and its surroundings now face deterioration of ecological environment, stagnation of tourism and poverty of residents.
▲规划进程:一个涵盖多个相关专业的专家工作组被建立起来,工作组对场地进行了细致的调研和数据收集,并且深入村落和社区广泛收集意见。Project promotion: A team of experts covering a number of related specialties was set up. The team conducted detailed investigation and data collection on the site, and went deep into villages and communities to collect opinions.
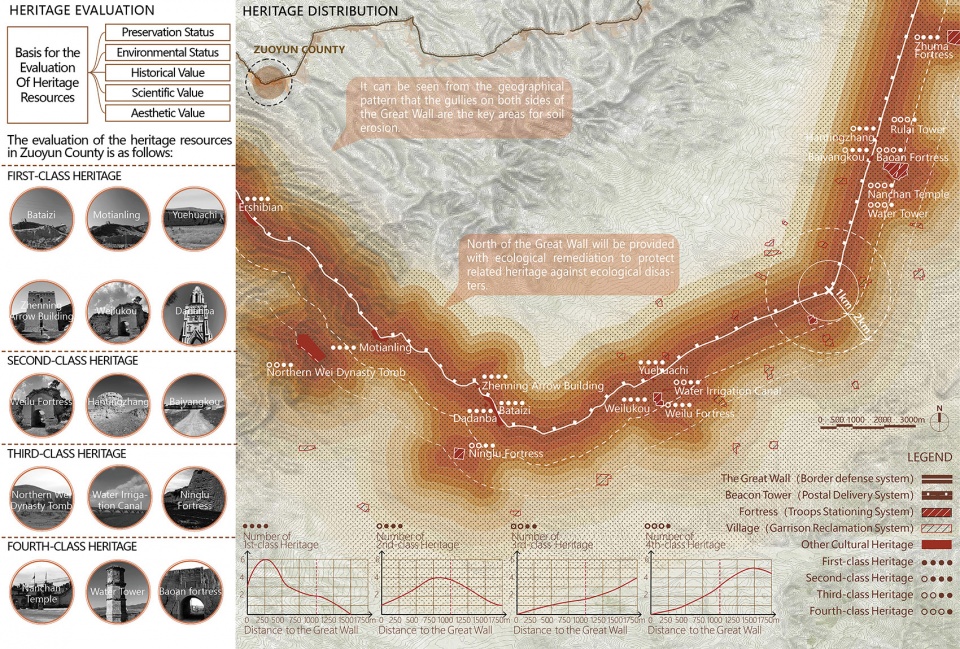
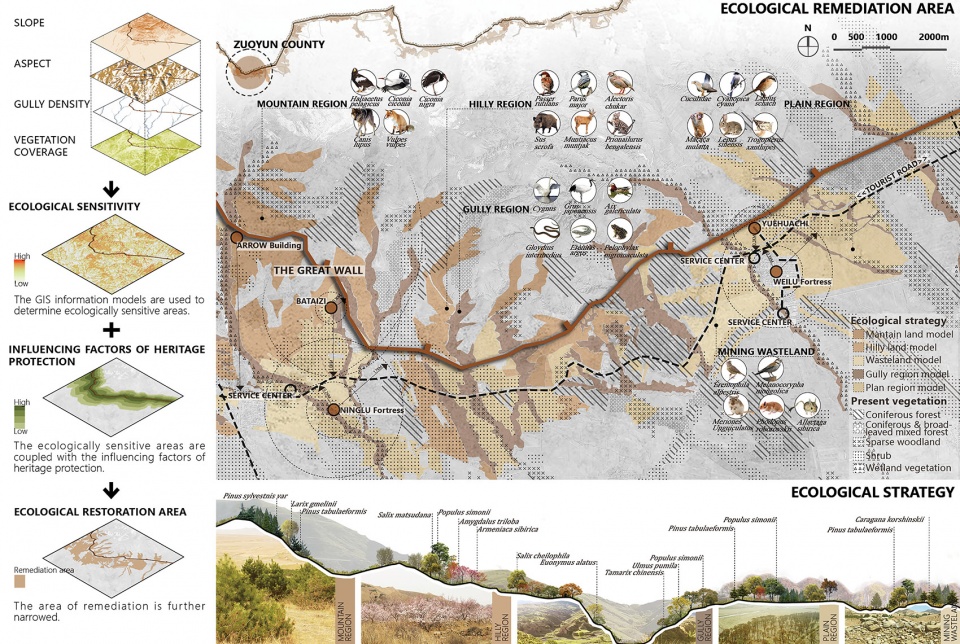
▲文化遗产的空间分布:通过对于古长城文化遗产的分析发现,高等级的遗产大多分布在距离长城1000m的范围内,这为确定遗产廊道的空间格局提供了依据。Distribution status of cultural heritage: Through the analysis of the cultural heritage of the Ancient Great Wall, it is found that the high class heritage is mostly distributed within the range of 1000m from the Great Wall, which provides a basis for determining the spatial pattern of the heritage corridor.
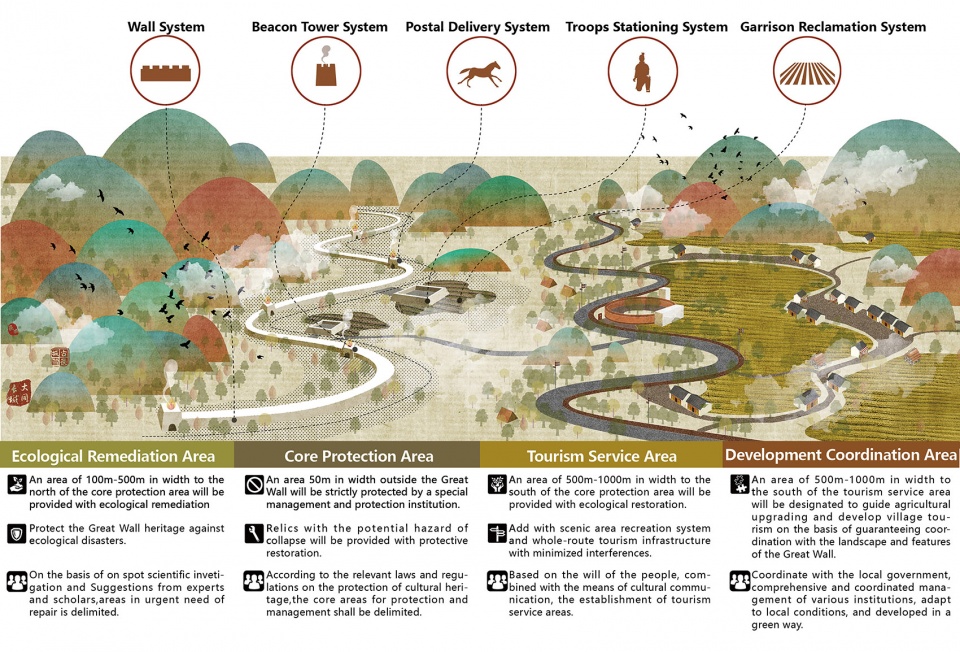
▲遗产廊道空间格局:依据长城及其周边五大类遗址的分布和保存现状,规划将古长城遗产保护的空间格局分为四个层级,以实现对于长城遗产的分级保护和发展。Relics protection: Based on the distribution and conservation status of the Great Wall and the five types of relics nearby, the planning has divided the spatial pattern for ancient Great Wall heritage protection into four levels, so as to realize the graded protection and development of the Great Wall heritage.
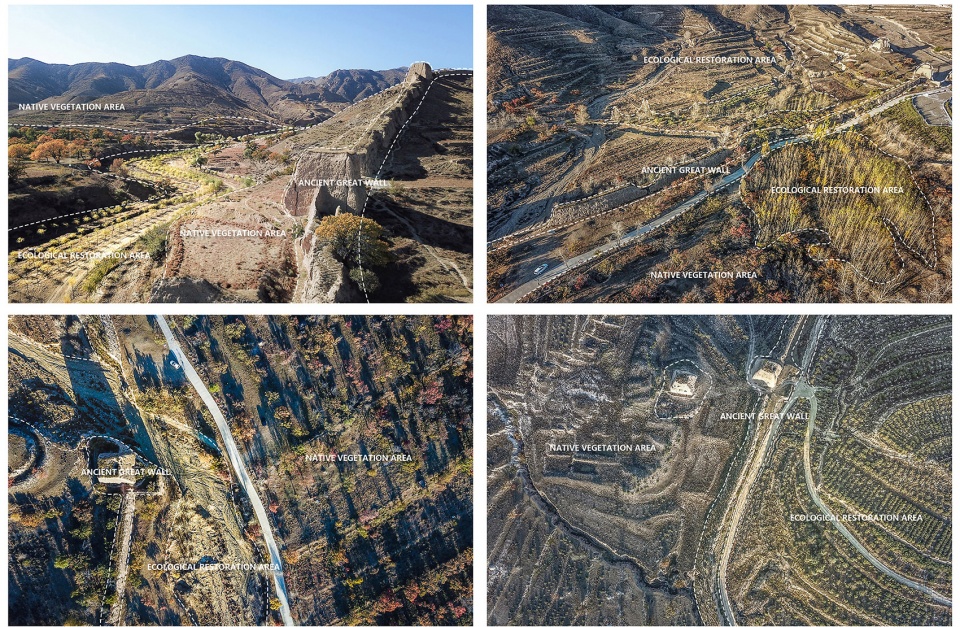
▲生态修复:通过科学的分析,一个集约有效的生态修复面域被确定下来。规划以当地原生植物群落为蓝本,在生态修复区构建低维护的人工植被群落,每个群落都考虑为动物提供相应的栖息地。Ecological remediation: A region for intensive and effective ecological remediation is determined. The planning takes local native vegetation community as blueprints, constructs artificial vegetation community requiring low-maintenance in area of ecological remediation, and provides habitats for animals in each community.
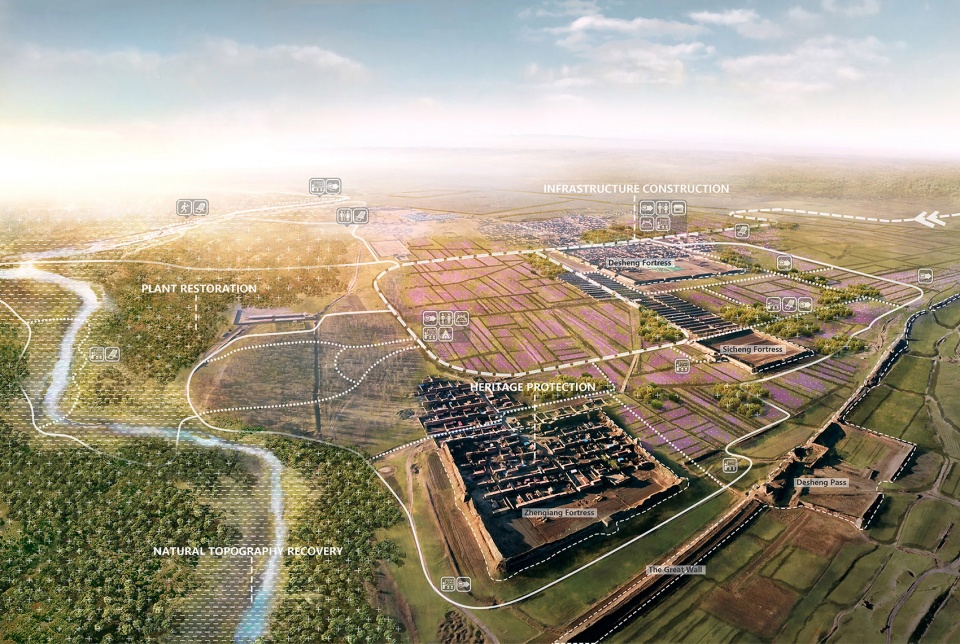
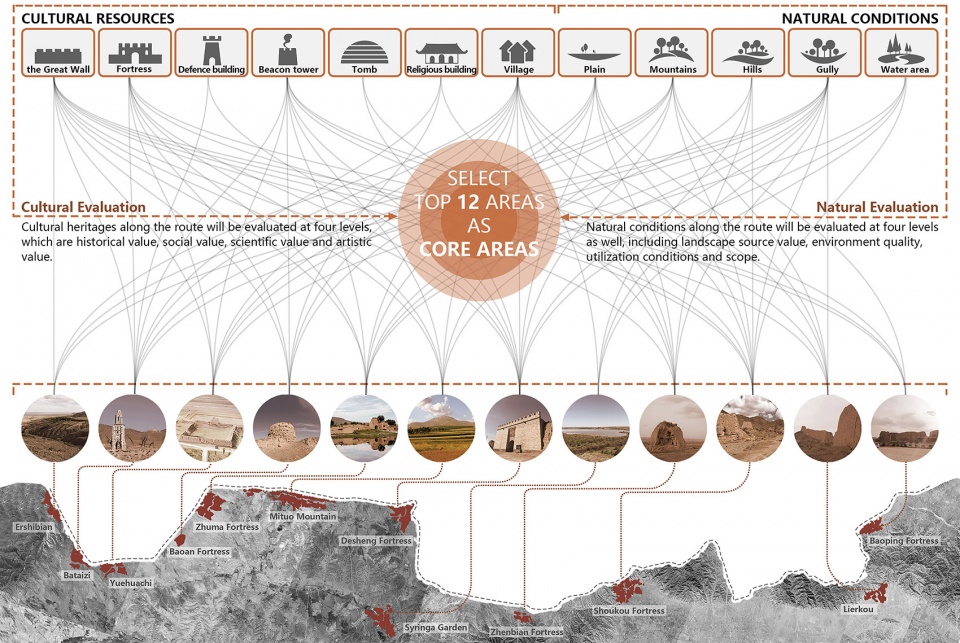
▲重点发展区域(景区)遴选:通过对长城沿线文化遗产和自然资源的评估和分级,确定了12个优质资源集中的区域作为重点发展区域(景区),作为整个遗产廊道的核心吸引物进行重点发展。Establishment of Approaches——Define the core area: The cultural heritages and natural resources along the Great Wall have been assessed and rated to determine 12 areas with concentrated high-quality resources as scenic areas for key construction as the core attractions of the entire heritage corridor.
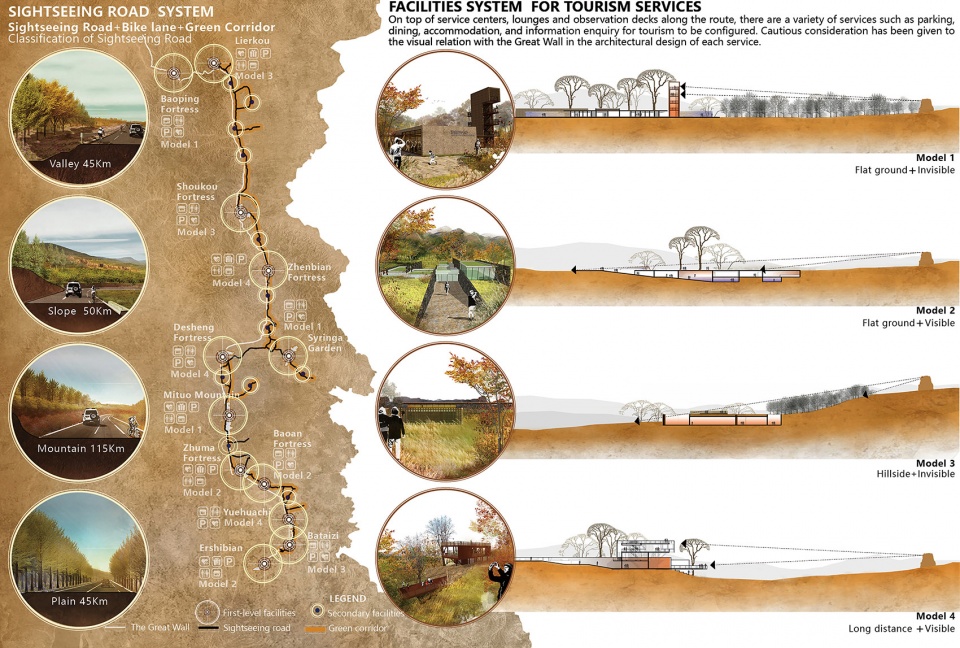
▲贯穿全线的慢行基础设施:一条全长255公里的旅游公路和自行车道将长城沿线串联起来,外侧设置弹性的带状绿廊;公路沿线设置12个驿站和若干休憩点,形成贯穿全线的慢行基础设施体系。Tourism facility system: A sightseeing road & bike lane system, 255km in total length, will be built to connect the Great Wall into an organic whole; a flexible belt-like green corridor will be constructed on the exterior; 12 service centers attached to the scenic areas will be set up along the road to create a continuous system of facilities for tourism services.
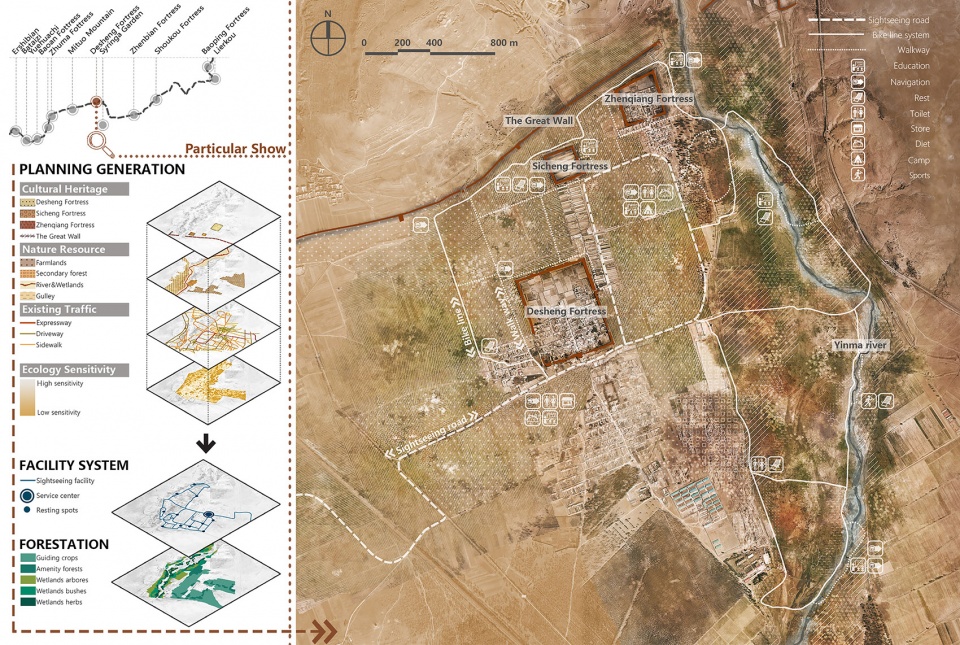
▲重点发展区域(景区)规划——得胜堡景区为例:为保证长城遗产不被干扰,景区内的生态修复和基础设施建设需要非常谨慎。经过科学的分析生态敏感度、遗产分布、现状基础设施等要素,一套低干扰的设施体系被建立起来。Scenic area planning——Desheng fortress as an example: To protect the historical features of the Great Wall, the vegetation restoration and tourism facilities in the scenic areas have been carefully considered. Based on a comprehensive analysis on ecological sensitivity, relics distribution, building suitability and other elements, a set of minimum interference schemes is established.
▲景区鸟瞰——得胜堡景区为例:景区内恢复自然地貌,构建独具地域特色的植被群落,形成秀丽的自然植物景观。建立游览步道、游客中心、休闲游憩、餐饮住宿等服务设施,配合导览、文化科普和自然科普设施,形成景区服务与解说系统。Scenic area birdview——Desheng fortress as an example: Through recovery of natural topography, such vegetation community with unique regional features could be created. A system of scenic area services and interpretation will be built, consisting of sightseeing trails, tourist service centers, leisure & recreation, dining & accommodation and other service facilities, supplemented by tour guides, and popularization facilities for culture and natural science.
▲景区内部——得胜堡景区为例:景区的生态环境将得以修复,所有服务设施的材料、颜色、形式都来自长城及其周边,使其低调的消隐在遗产环境之中。规划以增强现实技术(AR)再现长城历史的科普方式,游客在特定地点,可通过手机扫描二维码,显示出此处历史上某些特定场景与遗迹叠加的景象。Scenic area perspective——Desheng fortress as an example: The ecological environment of scenic areas is restored, and the layout, materials, colors and forms of all service facilities all come from the Great Wall and its surrounding areas and are blended in a low-key manner into the heritage environment. what’s more, the technique of Augmented Reality was introduced to reproduce the history scenes of the Great Wall.
▲村域产业引导:通过政府财政补贴、科技支持和规模化经营,引导农民种植实现增产增收;鼓励长城沿线村民能够通过参与建设、保护、维护和运营的方式,投入到文化遗产廊道全生命周期之中,让这些军垦戍边人的后代,依靠长城而改善了生活。Industrial Guidance: By means of fiscal subsidies from government, support by scientific research institution, operation of scales and so forth, rural people will be guided on the plantation to increase production yield and their income; villagers will be guided to develop folk tourism and introduce developers for investment and operation, in order to lift the local rural people out of poverty and make them better off.
▲项目进展——生态修复工程:经过一年多的建设,目前,总投资2.14亿美元的植被修复工程已经完成过半,近1.5亿株苗木被栽植在荒山、沟壑、谷地和平原上,为长城筑起了一道美丽的生态屏障。Current Achievements——Ecological Remediation: After a year of construction, the project of ecological remediation with a total investment of 214 million USD has been basically completed, nearly 150 million trees have been planted on barren mountains, ravines, valleys and plains, creating a beautiful ecological barrier for the Great Wall.
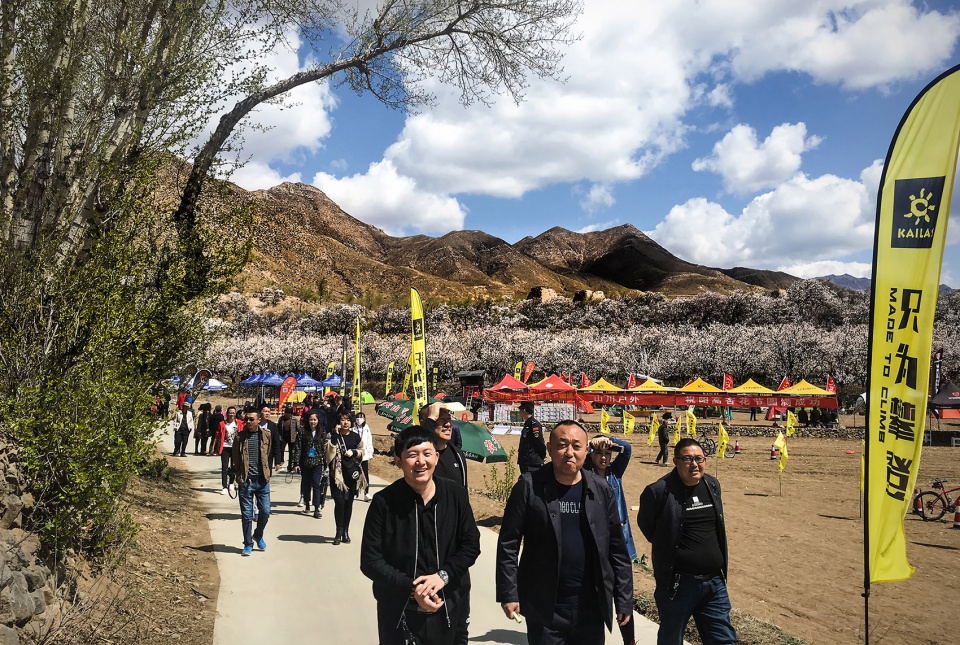
▲项目进展——慢行基础设施:沿古长城文化遗产廊道的旅游公路局部建成通车,个别景区已经对游客开放,盛开的杏花和充满魅力的长城吸引了大量游客前来观光。Current Achievements——Tourism facility system: The sightseeing road along the Great Wall have been partially put into use, some scenic area have been opened to tourists, the blooming apricot flowers and the charming Great Wall have attracted a large number of visitors.
▲项目总平面:通过激发长城遗产蕴含的能量,有望获得巨大的衍生效益。本规划协调了保护与发展、文化与生态、景观与社会等多个方面,可以预见的是,这一区域将因为长城的保护与可持续发展而复兴。Master plan: The planning has fully invigorated the derived benefits of cultural heritages, brought a balance to the benefits in a variety of aspects of protection and development, culture and tourism, industry and ecology etc., It’s foreseeable that this particular area will be revitalized as a result of the protection and flexible development of the Great Wall.
Project narrative
Background
Since ancient times, Datong sit at the boundary of nomadic peoples and agricultural peoples, and the Great Wall served as a defense system built up by agricultural peoples. People who are unfamiliar with the Great Wall usually take it as a giant wall; in fact, it’s much more complicated beyond imagination. In the Ming Dynasty, the Great Wall consisted of a wall system against enemies, a beacon-fire tower & postal delivery system for intelligence transmission, a troops stationing system for garrison duty and a garrison reclamation system for furnishing supplies; it was a huge and complete defense system. In the process of constructing and defending the Great Wall, numerous soldiers, laborers and their families settled down near the Great Wall and formed many settlements. With the fading of the threats posed by nomadic peoples, the Great Wall has gradually declined day by day as well.
Challenges
1 Relics protection
Due to its fragmented distribution, the Great Wall heritage has no continuous protection area. There is a lack of management over most parts of the Great Wall, and man-caused damages are widespread.
2 Ecological environment
Located in the interlaced zone of temperate grassland and temperate deserts, Datong has vulnerable ecological environment and sparse vegetation. In the Ming Dynasty, grass burning damaged the surrounding ecological environment of the Great Wall, and many parts of it collapsed due to soil erosion.
3 Approach to the heritage
There is not yet a continuous transportation system along the route of the Great Wall, Due to the failure of effective development and utilization of the resources of the Great Wall, there is a lack of scale, system and appeal in these scenic areas.
4 Social economy
Besides the low agro-economic benefits and the poverty of rural workers, there are also the outflows of young adults. The villages, habited by the elderly and children, are in ruins and depression.
Planning process
Considering the large scale and complex conditions of the project, we have built a planning team consisting of Landscape Architecture, GIS, Ecological Afforestation, Conservation of Water& Soil, Architecture, Cultural Tourism, Cultural Relics Protection among many other specialties, and hired members of local Great Wall protection associations and experts in botany and agro-economics to establish an advisory panel of experts.
The team have conducted detailed studies on historical materials, and carried out field surveys within the scope of planning for a duration of above two months and over a journey of above 2,000km. In combination with aerial images and land shot by UAV and databases of land resources and forestry information, the team have created a detailed GIS data model. What’s more, the team went deep into villages & communities, the opinions of the local people were widely collected.
Planning strategies
1 Relics protection
The cultural heritage assessment method has been employed to identify the spatial pattern for ancient Great Wall heritage protection. Through the analysis, it is found that the high class heritage is mostly distributed within the range of 1,000m from the Great Wall, based on that situation, we established the spatial pattern of the heritage corridor.
1.1 Core protection area
An area of 50m in width outside the Great Wall and its associated heritages will be strictly protected by a special management and protection institution, and relics with the potential hazard of collapse will be provided with protective restoration.
1.2 Ecological remediation area
An area of 100m-500m in width to the north of core protection area will be provided with ecological remediation to protect the Great Wall heritage against ecological disasters.
1.3. Tourism service area
An area of 500m-1,000m in width to the south of the core protection area will be provided with ecological restoration, and added with scenic area recreation system and whole-route tourism infrastructure with minimized interferences.
1.4 Development coordination area
An area of 500m-1,000m in width to the south of the tourism service area will be designated to guide agricultural upgrading and develop village tourism on the basis of guaranteeing coordination with the landscape and features of the Great Wall.
2 Ecological remediation
2.1 Determination of ecologically sensitive areas
The GIS information model was used to determine ecologically sensitive areas, and coupled with the influencing factors of heritage protection, the scope of remediation will be further narrowed.
2.2 Defining of Ecological remediation strategies
Adopting local native vegetation community as blueprints and targeting the natural characteristics of five types of ecologically sensitive areas, the planning has predefined matching models of planting, constructed basically vegetation community requiring low-maintenance and provided habitats for endangered species.
3 Establishment of Approaches
3.1 Selection of resources and determination of scenic areas
The cultural heritages and natural resources along the Great Wall have been assessed by grades and rated to determine 12 areas with concentrated high-quality resources as scenic areas for key construction.
3.2 Tourism facilities system
A sightseeing road & bike lane system, 255km in total length, will be built to connect the Great Wall into an organic whole; a green corridor will be constructed on the exterior to create a continuous recreation system, where full consideration will also be given to the overlooking relation with the Great Wall. 12 service centers attached to the scenic areas will be set up along the road to create a continuous system of facilities for tourism services. On top of service centers, there are a variety of services such as parking, dining, accommodation, and information enquiry for tourism to be configured. Cautious consideration has been given to the visual relation with the Great Wall in the architectural design of each service.
3.3 Scenic area planning
In the Scenic area, through the recovery of natural topography, the vegetation restoration and tourism facilities in the scenic areas have been carefully considered. A system of scenic area services and interpretation will be built, consisting of sightseeing trails, leisure & recreation, dining & accommodation and other service facilities, supplemented by tour guides, and popularization facilities for culture and natural science. Based on a comprehensive analysis on ecological sensitivity, relics distribution, building suitability and other elements and for the purpose of coordinating the features of the Great Wall heritage, careful consideration has been given to the layout, materials, colors and forms of all facilities in these scenic areas to blend them perfectly into the heritage environment.
4 Industrial guide
4.1 Agricultural guide
By means of fiscal subsidies from government, support by scientific research institution, operation of scales and so forth, rural people will be guided to plant oil plants, medicinal materials and other economic crops, so as to develop sightseeing agriculture and increase their income.
4.2 Village tourism development
Based on assessment of villages along the route, ancient villages with mature conditions will be moderately developed, and villagers will be guided to develop homestay hotels, rural tourism & dining, local specialty production & sales among other tourism services, in order to lift the local rural people out of poverty and make them better off.
Current Achievements
So far, the project of sightseeing road & ecological afforestation with a total investment of 360 million USD has been basically completed, some scenic area have been opened to tourists, the blooming apricot flowers and the charming Great wall have attracted a large number of visitors.
Conclusion
The planning has fully invigorated the derived benefits of cultural heritages, brought a balance to the benefits in a variety of aspects of protection and development, culture and tourism, industry and ecology etc., It’s foreseeable that this particular area will be revitalized as a result of the protection and flexible development of the Great Wall. What’s more, the project fully demonstrates that landscape architects can play a core role in such complex, large-scale projects which require cross-disciplinary collaboration.
规划设计团队:
本规划由北京林业大学园林学院、林学院、水土保持学院的师生和北京林业大学风景园林规划设计研究院(BLLA)的设计师通力合作完成,他们是(包括但不限于):
主持人:李运远、冯潇
总设计师:冯潇
总体规划:李运远、张云路
风景园林:赵晶、顿实、白桦琳、王宏达、税嘉陵、李爽、赵可极、陈思琪、王亚迪、刘昱含、程文宇、黄思成、武亚男
地理信息系统:王佳、张隆裕
生态修复:李国雷、史文辉、姚光刚
风景建筑:段威、周超
文化旅游:王忠君、吴若云
本规划在设计和实施的过程中,得到了大量来自大同市政府、大同市林业局、长城保护协会等机构专家和领导的支持,他们是(包括但不限于):
大同市政府:刘振国
大同市林业局:张宏东、武俊胜、宋昌、李辉、王杰、李建刚
山西长城保护协会:陈福仁